HTML
-
当今信息技术飞速发展的时代,推动着社会的进步,丰富着人们的日常生活。而信息作为数字化时代的必然产物,它的传输和存储受到了广泛的关注。目前,以光纤和电缆作为传输中介的网络已然成为了信息传递的主要技术,由于信息量的增大,传输速度的要求等,目前的传输方式遇到了挑战,因此,人们开始把目光转移到其他的传输方式,开启了新的载体的研究课题。
近几年来较为关注的课题是采用光子作为信息载体,利用原子相干技术实现量子信息。所谓原子相干效应就是量子干涉现象[1-4],通过光场与原子的相互作用,使得原子系统的能级之间发生关联,当加入强场的时候,原子能级发生劈裂、耦合等现象,形成新的叠加态,即多个跃迁通道。当原子发生跃迁时,将会产生吸收增强、吸收减少等情况,而跃迁通道之间发生的干涉即为量子干涉效应[5]。由于这一有趣现象的存在,人们开展了大量的研究,并取得了较好的工作,比如相干粒子数捕获(Coherent Population Trapping, CPT),控制光学双稳,电磁感应光透明(Electromagnetically Induced Transparency,EIT)[6-8],电磁诱导吸收(Electromagnetically Induced Absorption,EIA)以及相干光学烧孔现象等[9],这些科学进步必定促进科技发展,对未来相关领域的科学研究有着重要的指导意义。
文中将在铷原子蒸汽中建立四能级N模型原子系统,通过光路的设置、系数的合理调节,总结出加入强光和弱光后光谱的吸收特点,为这一技术的应用提供理论基础。
-
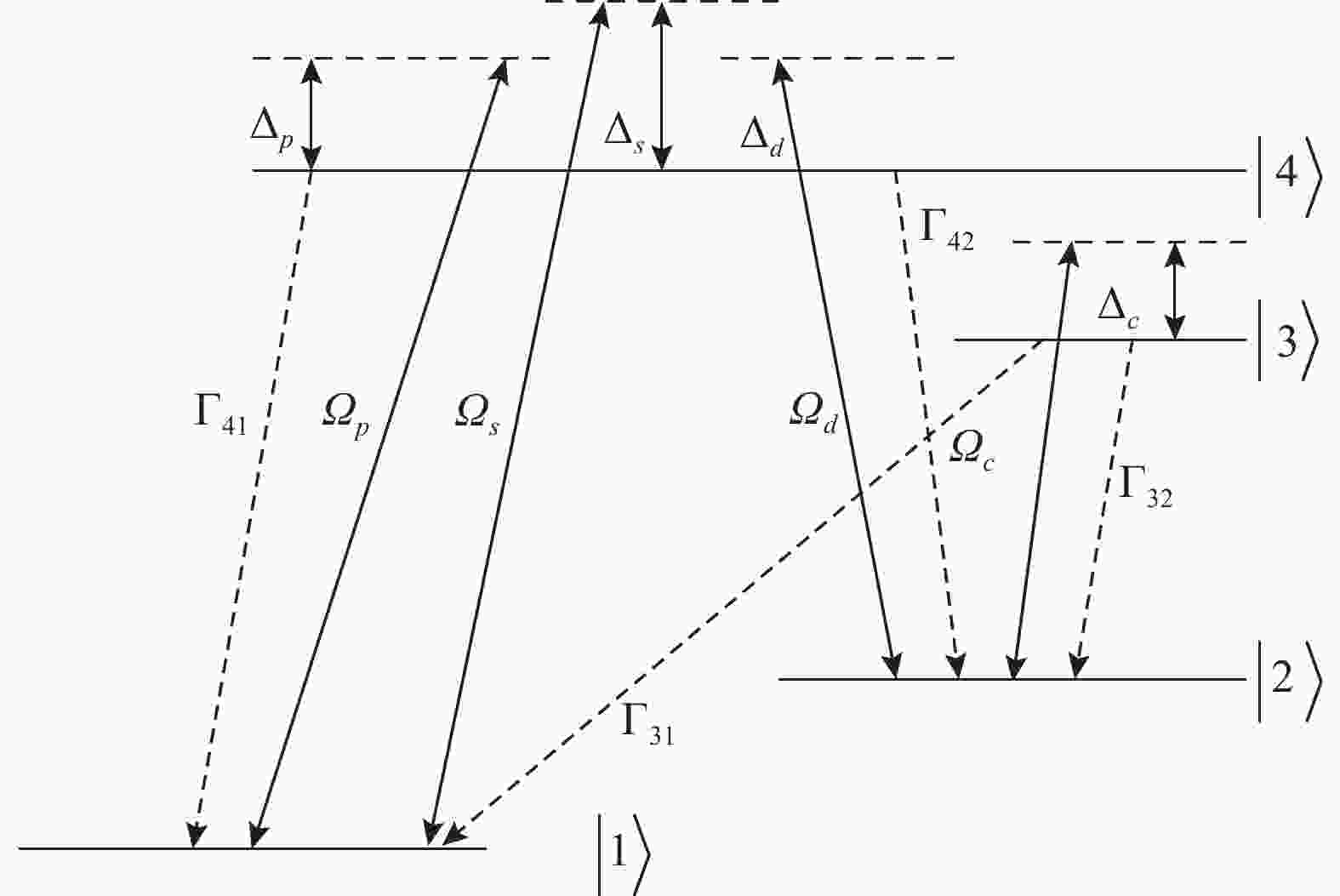
在如图1所示的原子系统中,同时引入一束饱和光和一束探测光,频率分别表示为
${\omega _s}$ 和${\omega _p}$ ,其中饱和光用来激发原子,探测光较弱,用来观察原子系统与光场作用后的吸收情况;在模型中,还引用两束耦合光,分别为${\omega _c}$ 和${\omega _d}$ ,其作用是使得不同能级之间发生耦合现象。以上四束光所加的位置如图中所示,失谐关系如下:两束耦合光失谐分别为${\Delta _c} = {\omega _c} - \left( {{\omega _3} - {\omega _2}} \right)$ 和${\Delta _d} = {\omega _d} - \left( {{\omega _4} - {\omega _2}} \right)$ ;探测光和饱和光失谐为${\Delta _p} = {\omega _p} - {\omega _4}$ 和${\Delta _s} = {\omega _s} - {\omega _4}$ ;饱和光、两束耦合光拉比频率分别为${\varOmega_s} = {E_s}{\mu _{14}}/2\hbar$ 、${\varOmega _c} = {E_c}{\mu _{23}}/2\hbar$ 、${\varOmega _d} = {E_d}{\mu _{24}}/2\hbar $ 。根据模型设计的已知条件,且由于探测光较弱,笔者此时忽略它对于整个原子系统产生的影响,可以获得在薛定谔图像下的哈密顿量,进而推出相互作用图像下的表达式,再由密度算符运动方程得出密度矩阵。最后通过拉氏变换法和量子回归理论,同时考虑多普勒效应,得出探测光的吸收谱表达式[10]:${N_0}$ 为单位体积内原子数;$u$ 为最可几速率。 -
文中,笔者将采取不同的光路安排,通过光场参数的调整,完成模型的演化,观察探测光吸收光谱的形成特点,总结规律,分析原因,得出数值模拟结果。
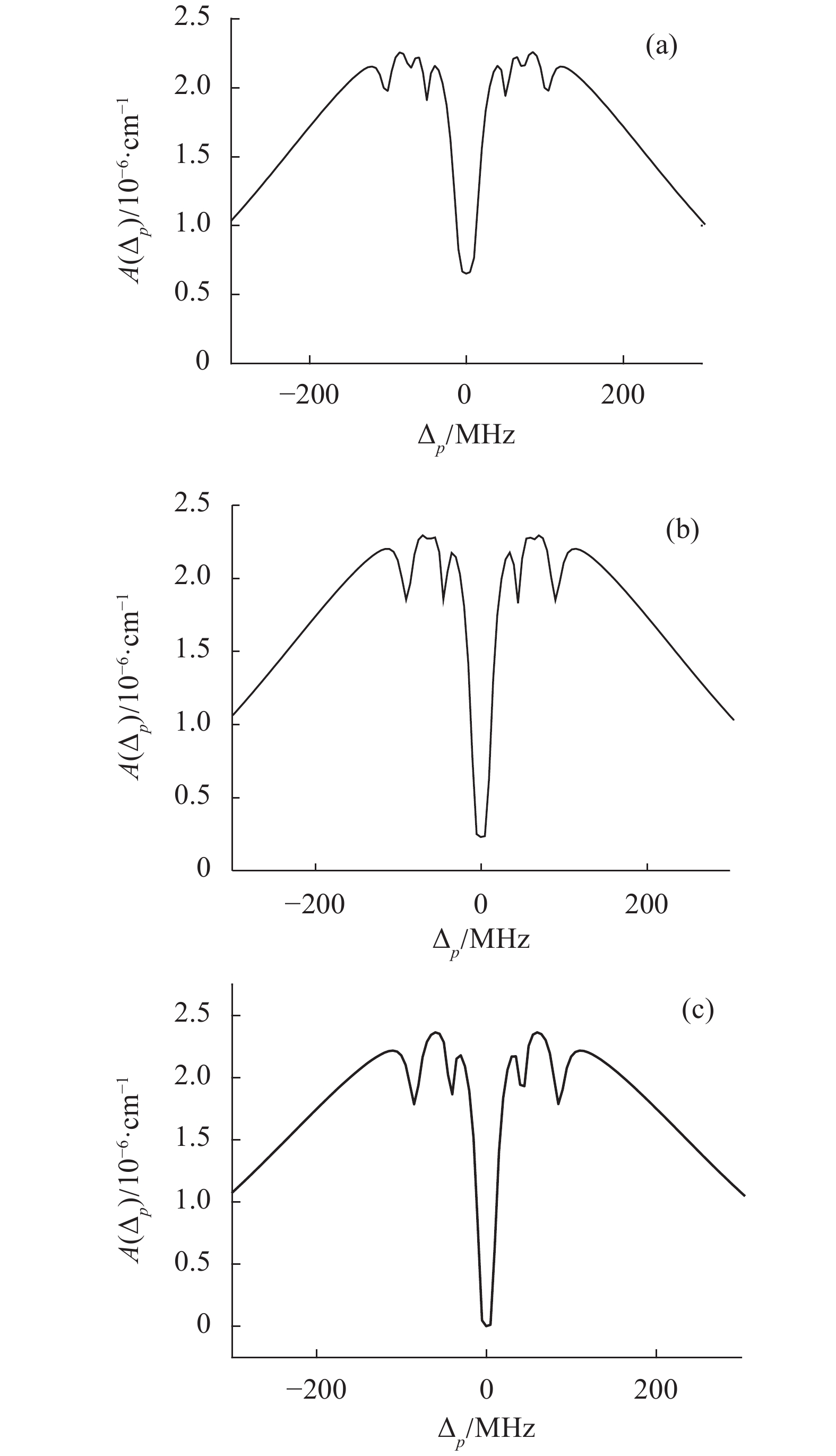
(1)耦合光
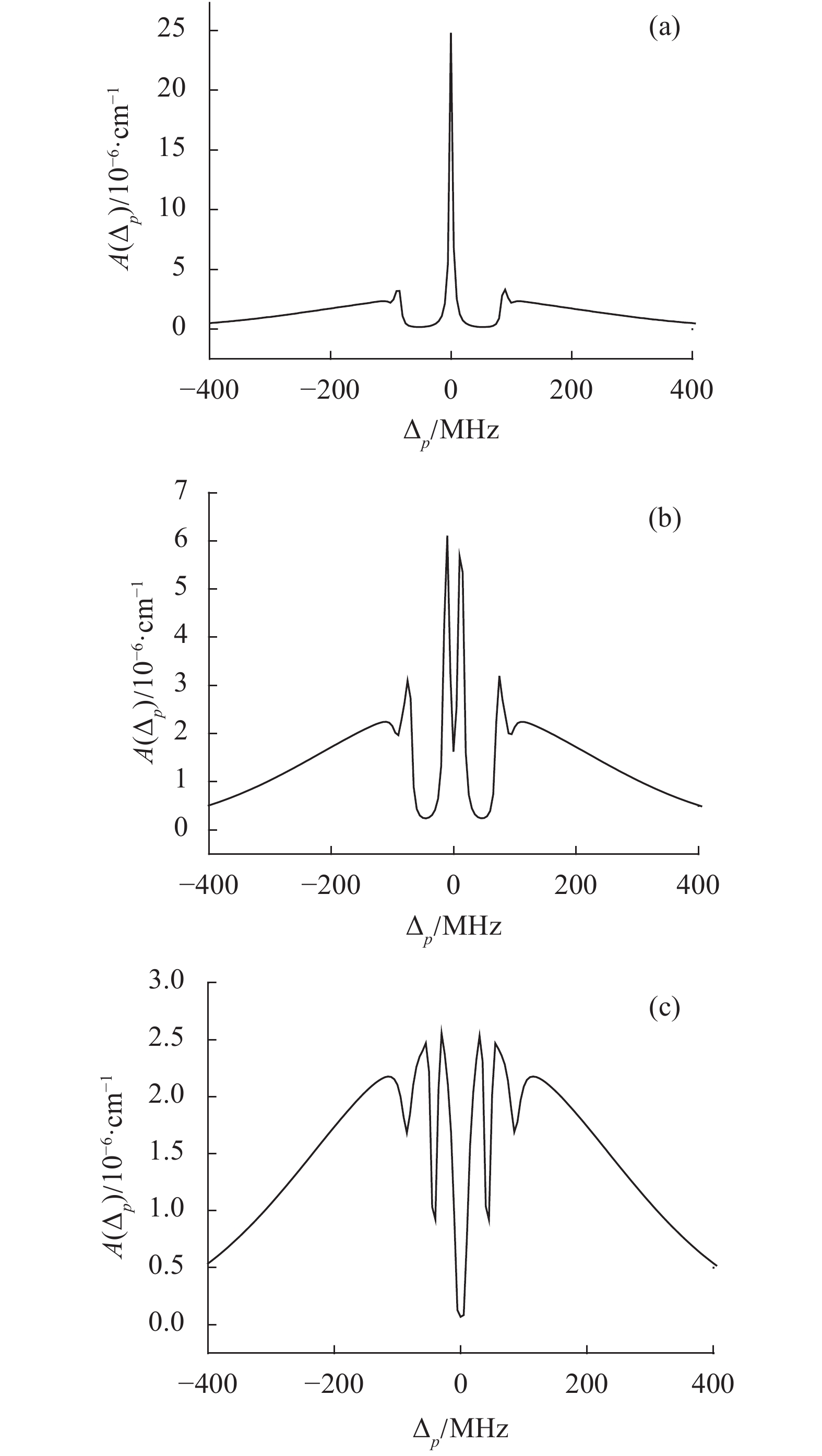
$c$ 和$d$ 与探测光$p$ 同向传播,与饱和光$s$ 反向传播。其中:${\varOmega _s} = 3\;{\rm{MHz}}$ ,${\varOmega _d} = 60\;{\rm{MHz}}$ ,${\varOmega _c} = 40\;{\rm{MHz}}$ 。如图2(a)所示。此时,由于两束耦合光$c$ 、$d$ 分别作用在$\left| 2 \right\rangle \leftrightarrow \left| 3 \right\rangle $ 和$\left| 2 \right\rangle \leftrightarrow \left| 4 \right\rangle $ 能级之上,导致能级发生劈裂,重新叠加,而饱和光同时激发三群原子,对应六个共振吸收峰,所以在图像中可以看到对称的六个下凹为六个相干光学烧孔;由于此时的光路安排使得探测光和耦合(${\gamma _{41}} \!= \!3\;{\rm{MHz}}$ ,${\gamma _{_{42}}} \!= \!3\;{\rm{MHz}}$ ,${\gamma _{43}} \!= \! 3\;{\rm{MHz}}$ ,${\gamma _s} = 0.01\;{\rm{MHz}}$ ,${\upsilon _p} = 250\;{\rm{m/s}}$ ,${\Delta _s} = {\Delta _c} = {\Delta _d} = 0$ ${\lambda _{41}} = {\lambda _{42}} = {\lambda _{32}} = 794\;{\rm{nm}}$ 以下图参数均相同)光处于相消多普勒现象,因此在中间出现了吸收减少的电磁感应光透明窗口EIT。同时,以往的研究表明[10],该相干光学烧孔的深度和位置都可以根据需要调节。当保持饱和光$s$ 拉比频率${\varOmega _s} = 3\;{\rm{MHz}}$ 不变,耦合光$d$ 的拉比频率${\varOmega _d} = 60\;{\rm{MHz}}$ 不变,将耦合光$c$ 的拉比频率减少到${\varOmega _{{c}}} = 20\;{\rm{MHz}}$ 时,得到的数据模拟如图2(b)所示。相干光学烧孔和EIT的数量没有变化,只是两侧的烧孔与次两侧的烧孔相比较出现加深,而次两侧的烧孔出现变浅的现象。这是由于减少了加在$\left| 2 \right\rangle \leftrightarrow \left| 3 \right\rangle $ 跃迁之上的耦合光拉比的频率,从而减少了两个能级之间的相干性,而相对的$\left| 2 \right\rangle \leftrightarrow \left| 4 \right\rangle $ 之间的原子相干性显示加强。当饱和光$s$ 和耦合光$d$ 拉比频率仍然不变,继续减少耦合光$c$ 的拉比频率直至零,得到探测光的吸收谱如图2(c)所示。在图中可以看到,此时只剩下一个EIT窗口和四个相干光学烧孔。这是因为,当耦合光$c$ 的拉比频率减小到零时,原子模型发生了变化,能级$\left| 2 \right\rangle $ 与能级$\left| 3 \right\rangle $ 解除了关联,相干性消失,模型转换为三能级$\Lambda $ 型,此时饱和光只能激发二群原子,形成四个共振吸收峰,因此出现四个相干光学烧孔。相对的情况,当保持饱和光$s$ 和耦合光$c$ 的拉比频率不变,而改变耦合光$d$ 的拉比频率。其中:${\varOmega _s} = 3\;{\rm{MHz}}$ ,${\varOmega _C} = 60\;{\rm{MHz}}$ ,${\varOmega _d} = 50\;{\rm{MHz}}$ 。如图3(a)所示,与图2(a)中的参数相比,饱和光没有变化,耦合光$d$ 减小,则吸收谱中无论是相干光学烧孔还是EIT窗口均变浅,均可见,此时$\left| 2 \right\rangle $ 、$\left| 4 \right\rangle $ 能级之间的耦合光拉比频率的减小使得整个原子系统的原子相干效应减弱。当笔者继续减小耦合光$d$ 的拉比频率直至为零时,如图3(b)所示。在图中只有在${\Delta _p} = 0$ 处出现一个下凹,由于耦合光$d$ 的拉比频率减少为零,即原子模型中相当于失去了耦合场的作用,没有了相干性,因此判定下凹是由于饱和光的作用,激发原子,而得到了传统的光学烧孔。而烧孔的这一有趣的物理现象对于光在信息存储中的应用有着重要的研究价值,因此数量的多少也是很有意义,所以根据上诉内容,在原子系统中耦合场有着至关重要的作用。(2)耦合光
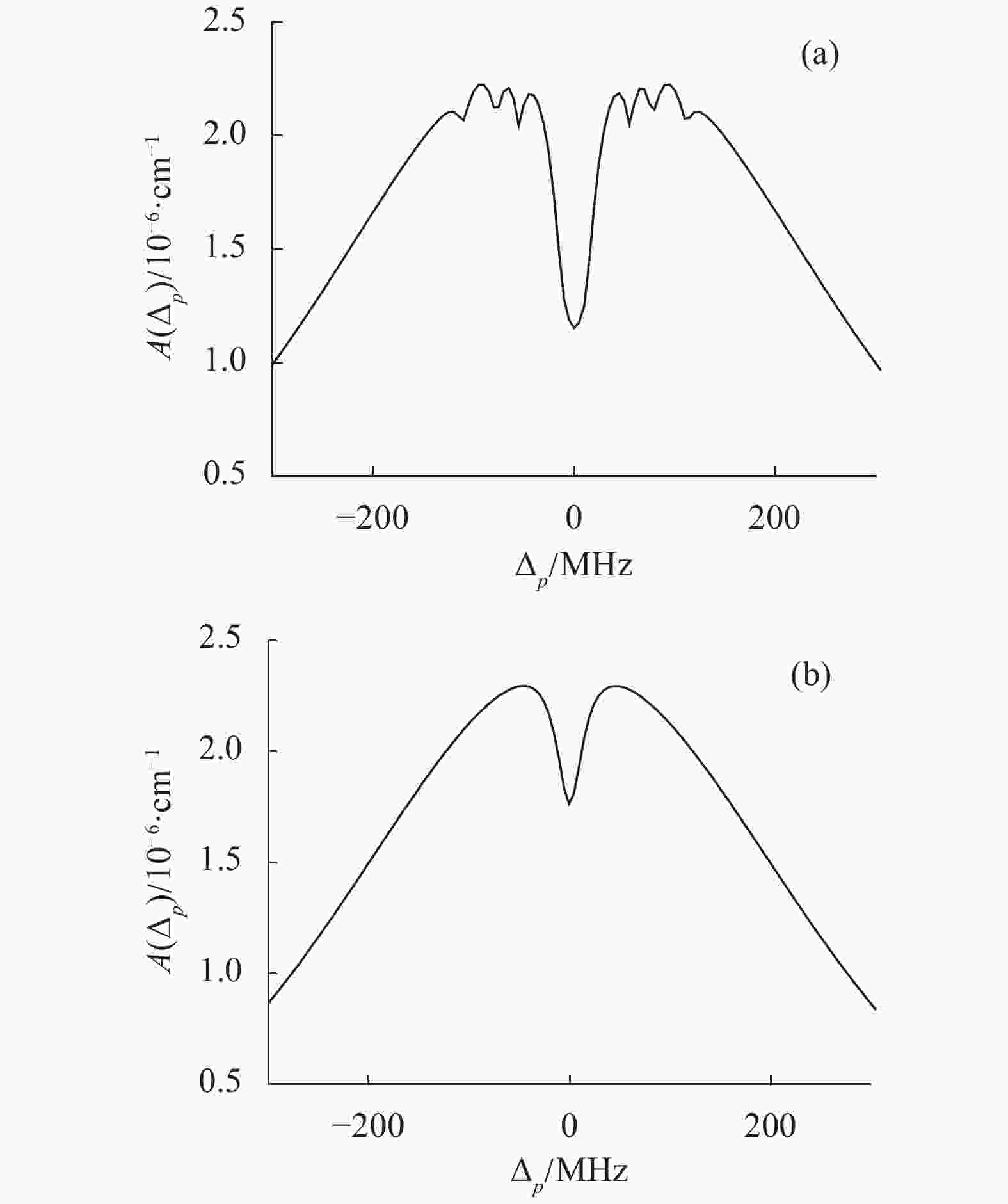
$c$ 、$d$ 分别与探测光$p$ 反向、同向传播,饱和光$s$ 与探测光$p$ 反向传播。当${\varOmega _s} = 6\;{\rm{MHz}}$ ,${\varOmega _c} \approx {\Omega _d}$ ,${\varOmega _c} = 50\;{\rm{MHz}}$ ,${\Delta _s} = 0$ ,如图4(a)所示。从图中较为显著的是在${\Delta _p} = 0$ 处出现的较大的是由于光跃迁诱导的原子相干导致的吸收增强效应,电磁诱导吸收EIA,两侧是两个较小的吸收增强。同时在中间吸收增强的两侧还有两个较宽的下凹,即由于量子相干效应引起的吸收减少EIT,此时系统中同时出现EIT和EIA。根据烧孔的形成特点,这样的光路安排应该出现四个相干光学烧孔,很明显,有两个烧孔落入了图中的EIT窗口中,其他两个分布在两侧。当保持其他不变,${\varOmega _{{c}}} = 30\;{\rm{MHz}}$ 时,如图4(b)所示。${\Delta _p} = 0$ 处出现了新的EIT窗口,而两侧的变窄。当${\varOmega _{{c}}} = 0\;{\rm{MHz}}$ 时,如图4(c)所示。此时吸收峰基本消失,较为明显的是下凹出现深而窄的现象。这是由于耦合光$c$ 的消失,改变了模型的结构,$\left| 2 \right\rangle \leftrightarrow \left| 3 \right\rangle $ 之间的关联解除,模型再次演化成为由$\left| 1 \right\rangle $ ,$\left| 2 \right\rangle $ ,$\left| 4 \right\rangle $ 构成的三能级$\Lambda $ 型,因此两侧的四个下凹均为相干光学烧孔,原来的三个EIT窗口也只剩中间一个,且无论是此时的EIT还是相干光学烧孔均较为清晰,且深而窄,为后续在其中实现光速减慢提供有利保证。 -
文中针对两束耦合光、一束饱和光和一束探测光三束相干光场构成的N模型原子系统进行了细致的讨论。讨论分成两种传播方式,其中一种传播方式下,通过光场的方向、强度,从数值模拟比较,得出耦合光的引入加强了能级之间的关联性,从而加强原子的相干特性,很好地调节模型之间的转换,从起初的N模型到三能级
$\Lambda $ 原子模型到普通的二能级原子模型,从形成相干光学烧孔的数量、形成原因到普通的光学烧孔,展示完整的过程,总结了模型之间的关联性;在另一种传播方式下,通过耦合光强度的调节,可以在吸收谱中同时出现EIT、EIA两种有趣的物理现象,以及烧孔深度、EIT的透明深度以及EIA的强度等。上述研究对于EIT、EIA相关的光学存储、光学开关等方面具有重要的参考价值。


























































































 DownLoad:
DownLoad: