-
随着世界各国对海上军事装备的加强,对于舰船、航母、核潜艇的侦查显得尤为重要,舰船尾流的识别受到了国内外学者的广泛关注。海军工程大学[1]设计研制并验证了基于后向散射的光尾流探测方法的可行性;万俊等[2]采用盲源分离和独立成分分析的方法对水体与气泡尾流后向散射光信号进行分离,但得到的信号噪声对判决结果有很大影响;彭晓雷等[3]通过对气泡回波信号的后沿位置、峰值大小和位置等脉冲特征进行统计分析,实现了对气泡的识别,但由于采集数据多造成脉冲特征统计过于繁琐;梁善勇等[4]利用回波强度、偏振信息等实现对舰船尾流的探测识别。综上可以看出,目前采用激光雷达对舰船尾流的识别主要依靠回波信号特征和偏振信息[2-4]等,这些方法是对探测结果较为明显的单帧回波信号进行特征提取,并未对连续采集的多帧动态回波信号进行分析。
水中气泡群对激光有很强的后向散射效应[5],入射到气泡表面与透过气泡群的回波信号有很大差别。气泡直径、密度、运动速度时刻变化,使得回波信号处于一个非线性、非稳态状态[6],导致气泡群回波信号特征不稳定。因此,利用传统方法对非稳态的尾流回波信号进行特征提取和识别,存在很大的局限性。
针对以上问题,文中提出了基于主分量分析法 (Principal Component Analysis, PCA)[7]与弹性BP (back propagation)神经网络结合的水下气泡识别算法。通过自主设计的水下激光雷达探测系统进行室内模拟实验,针对非稳态的回波信号进行数据预处理得到满足条件的高维特征矩阵,利用主分量分析法对预处理后的拼接样本进行特征提取,采用弹性BP神经网络进行水下气泡识别,可有效解决连续采集的非稳态回波信号特征提取困难和识别率低的问题。实验结果表明,该算法在减少识别时间的同时,对气泡群有较好的识别效果。
-
实验数据经笔者所在实验室自主研发的水下单元APD激光雷达探测系统得到,如图1(a)所示为搭建的激光雷达室内气泡群探测平台,主要分为3个部分:lidar系统结构、水池环境、数据采集结构。数据采集结构包括采样频率为500 MHz的AD采集卡和计算机。水池环境包括内壁贴满黑色卡纸的透明玻璃水池(0.48 m×0.67 m×3.70 m),水深0.36 m,激光探测高度0.26 m。利用电磁式空气压缩机与增氧气盘产生气泡,气泡直径约为10~200 μm,并用气阀对气流量进行调节。雷达系统指标参数见表1。

Figure 1. Experimental device for data acquisition of underwater bubbles; (b) Photo of the underwater lidar system (inside the metal box); (c) The laser runs through the bubbles without background light; (d) Air pump (voltage: 220 V, frequency: 50 Hz, power: 60 W, transmission volume: 50 L/min); (e) Bubbles plate (the diameter of the air bubbles is about 10-200 μm); (f) Valve: control airflow
Parameter Value Parameter Value Wavelength/nm 532 Receiving diameter/mm 80 Pulse width/ns 10 Emission diameter/mm 20 Pulse energy/mJ 10 Emission angle/mrad 1.7 Center distance/mm 100 Receiving angle/mrad 2.5 Table 1. System parameters
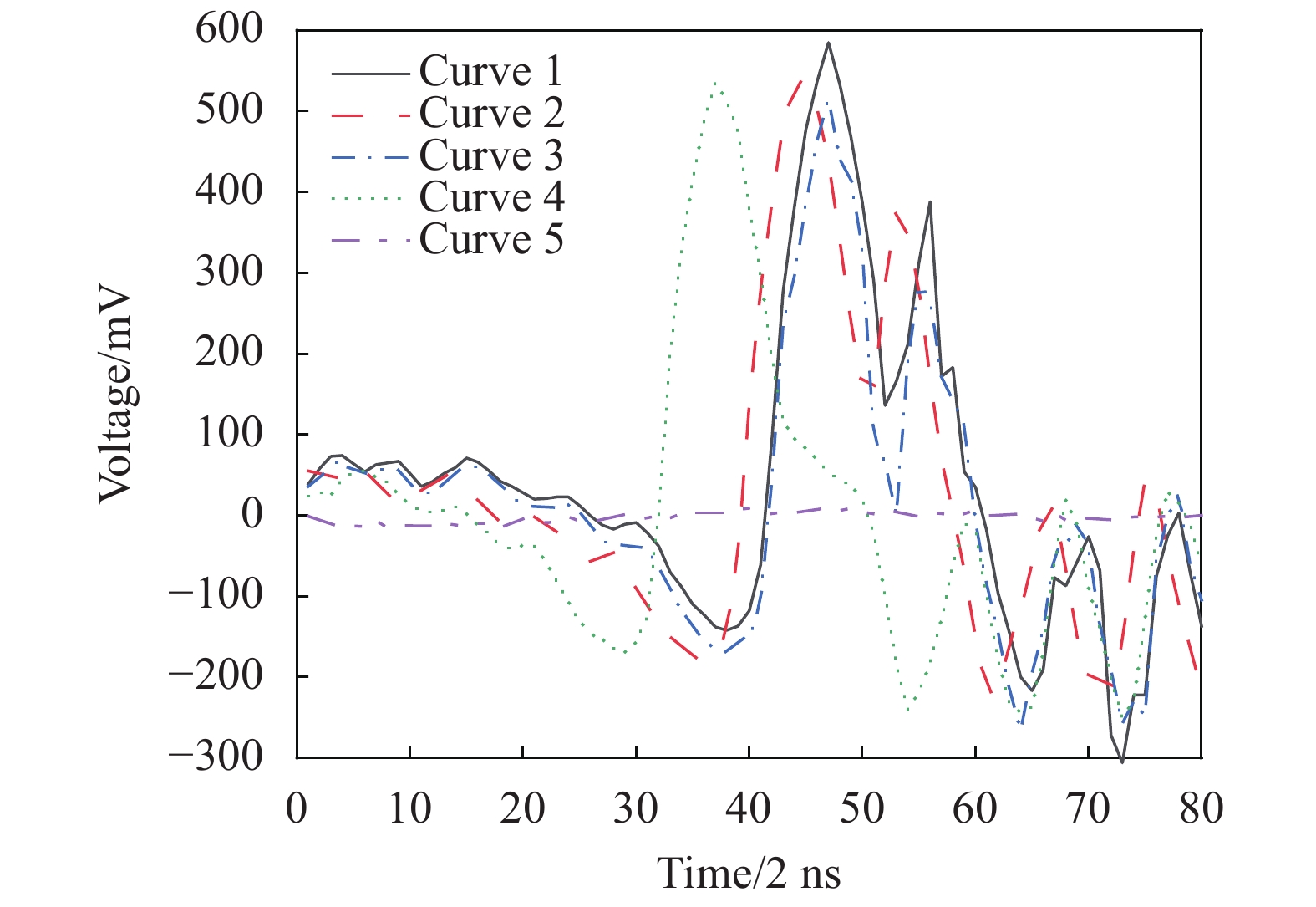
在测量过程中,信号的起始时间由激光器内触发信号决定,回波信号是以512个采样点为一个周期的连续一维曲线。系统对位于2.8 m处的气泡群进行连续探测,将前5个周期的有效回波信号截取出来,如图2所示。曲线1、2、3呈双峰分布,表明此刻激光系统探测到气泡群回波,由于激光器、AD采集卡具有一定延时以及气泡群的运动,导致回波信号产生时间起点上的相对漂移,连续采集的回波信号在幅值和峰值位置具有一定差异;曲线4呈单峰分布,即只有水体回波信号,由于系统的低采样率和气泡群的非稳态特性,造成此刻未接收到气泡群回波信号,这类数据的存在降低了气泡群回波信号的识别率;曲线5没有回波峰,为无效数据,需在预处理中去除。因此,数据中存在有气泡群回波峰的信号、无气泡群回波峰的信号和空采的无效数据等。与传统的经过人为选择方式得到满足条件的单帧回波信号相比,文中得到的原始数据与实际舰船尾流探测得到的回波信号更加接近,对该情况下的气泡群回波进行探测识别更具有实用性。
对目标回波信号的特征提取一直是进行目标识别与分类的主要技术[8-9],回波漂移、采样率低和无效采集等问题对于气泡群的识别有极大影响,因此必须对测量结果做相应的预处理,具体步骤如下:
(1)原始数据分段切片。根据水池长度及回波信号时间漂移量可知,回波信号主要集中在前80个采样点,为实现后续的波形平移,因此,截取每个分段的前100个采样点作为单次采集的有效数据,共采集N组数据。
(2)去除无效数据。首先将各组数据中小于零值的强度置零,求得峰值求平均值
$ E\left( x \right)$ ,确定峰值有效范围,若超出有效范围,则去除该组数据。经多次实验,有效范围为$ \left( {1 \pm 0.5} \right) \times E\left( x \right)$ 时,可对无效数据进行有效去除。(3)波形平移。设第i次采集的信号为
$ x\left( i \right)$ ,峰值位置为$ a\left( i \right)$ ,找到N组数据中峰值位置最大值MAX和最小值MIN,设基准点为$ n$ ,满足公式(1)的条件。每次以步长1增加,寻找最优基准点使得各$ a\left( i \right)$ 与基准点$ n$ 的平方差$ E\left( n \right)$ 达到最小,最后将$ x\left( i \right)$ 按$ a\left( i \right)$ 与$ n$ 的相对距离在时域上进行左右平移,数据空位按零值补位。(4)阈值处理。在不失真的前提下选择强度阈值,将小于阈值的置零,减少噪声的影响,文中的阈值为最大峰值的5%。
(5)将定长的矢量数据按采集时间顺序进行拼接,形成一个高维特征矩阵。
-
PCA是将多个指标化为少数几个综合指标来代替原始数据中较多的变量的统计方法,而且所含信息互不重复。为验证该算法的识别能力,在实验中增加一类干扰目标(透明玻璃板),将其置于气泡群所处的位置,得到其回波信号与气泡接近。分别对距离激光雷达2.2 m的无气泡、气泡、透明玻璃板3类目标进行连续1 min测量,测得的回波信号组数分别为589、593、578;然后对各组数据进行预处理,得到有效数据各为545、560、569;随机选取其中各300组数据,每组数据按行排列,以100个采样点作为每组数据的特征维数,最后得到由维数100的900组数据拼接组成的高维样本矩阵X900×100。
为选取能有效识别的特征,利用PCA算法对样本矩阵进行降维处理,特征值以权重大小依次往后排列。一般认定当前n个特征值累计权重值足够大,可取前n个主分量作为提取后的样本特征向量。
为最大化减少特征维数,选择前2个特征值的得分,第1个作为横坐标,第2个作为纵坐标画离散图,如图3所示。气泡主要分布于PC1轴正半轴区域,无气泡和玻璃板主要分布于PC1轴负半轴区域,除个别没有完全分离以外,3类目标基本分为3个部分,且气泡与非气泡的区别比较明显。通过前2个主成分可以将气泡识别出来,说明将预处理后的数据拼接为高维样本矩阵,利用PCA进行特征提取是有效的。
-
BP神经网络[10]以其能够处理知识背景模糊、环境信息复杂等系列问题, 被广泛应用于信号处理、模式识别等领域。
目前,弹性梯度下降法能有效避免梯度大导致收敛速度慢的问题[11]。为消除梯度幅度的影响,权值修正时仅与梯度的符号有关,2次迭代的梯度方向决定权值大小。梯度方向相同时,权值的修正值乘以一个增量因子;相反时,乘以一个减量因子;梯度等于零时,保持不变。权值修正的更新公式为:
式中:gra(i)为第i次迭代的梯度;
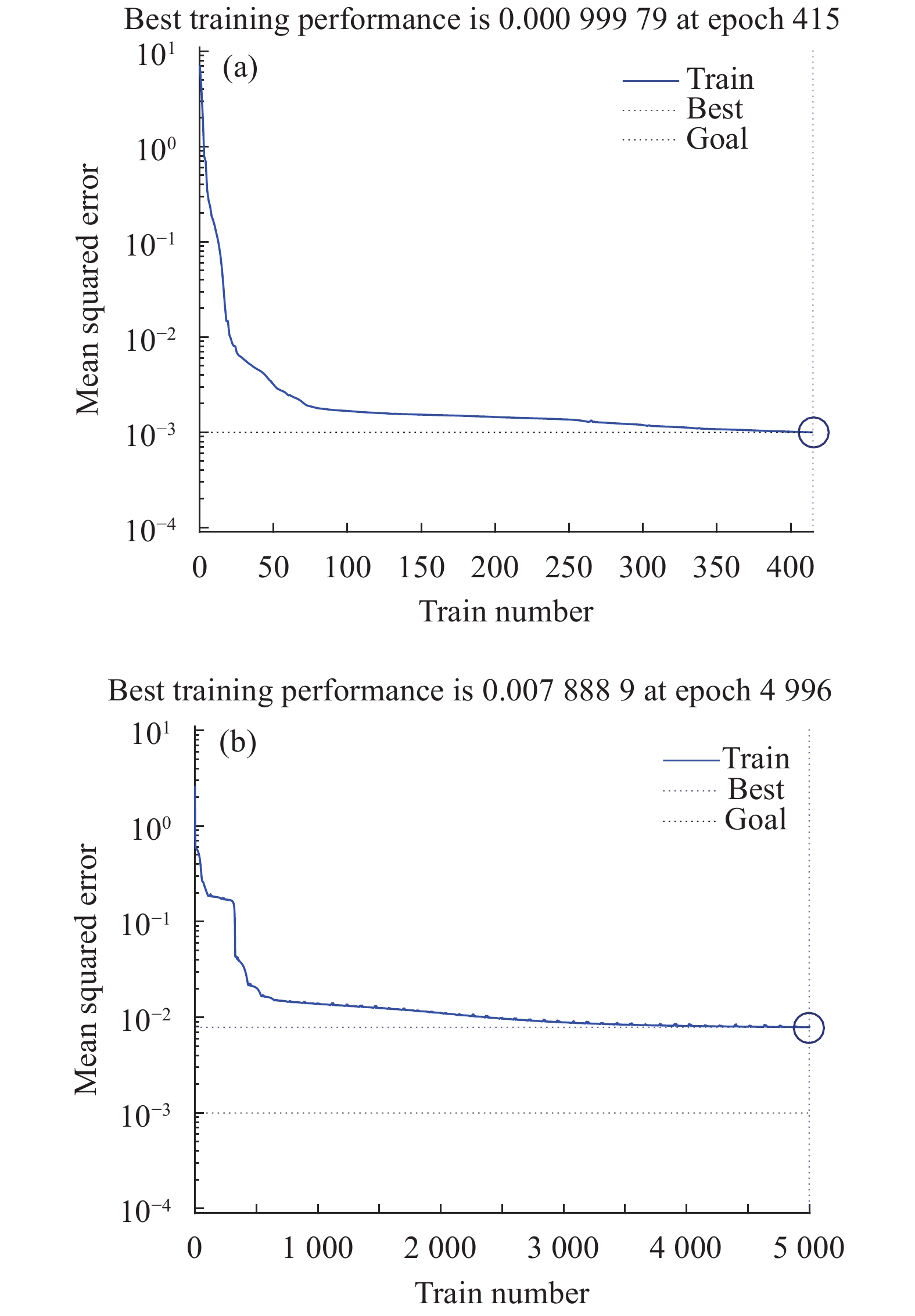
$ \alpha $ 为增量因子;$ \;\beta$ 为减量因子,$ 0 < \beta < 1 < \alpha $ 。在相同条件下,设定目标函数为0.001,迭代5000次,得到弹性BP算法和自适应学习与附加动量BP算法[12]随迭代次数的增加的收敛情况,如图4所示,横坐标为训练次数,纵坐标为归一化后数据的均方误差。弹性BP算法在迭代415次时就达到目标,而自适应与附加动量BP在迭代4996次时还未达到目标函数,弹性BP算法收敛速度快且收敛性更好。

Figure 4. Iterative convergence of different algorithms. (a) Elastic BP algorithm; (b) Adaptive and additional momentum BP algorithm
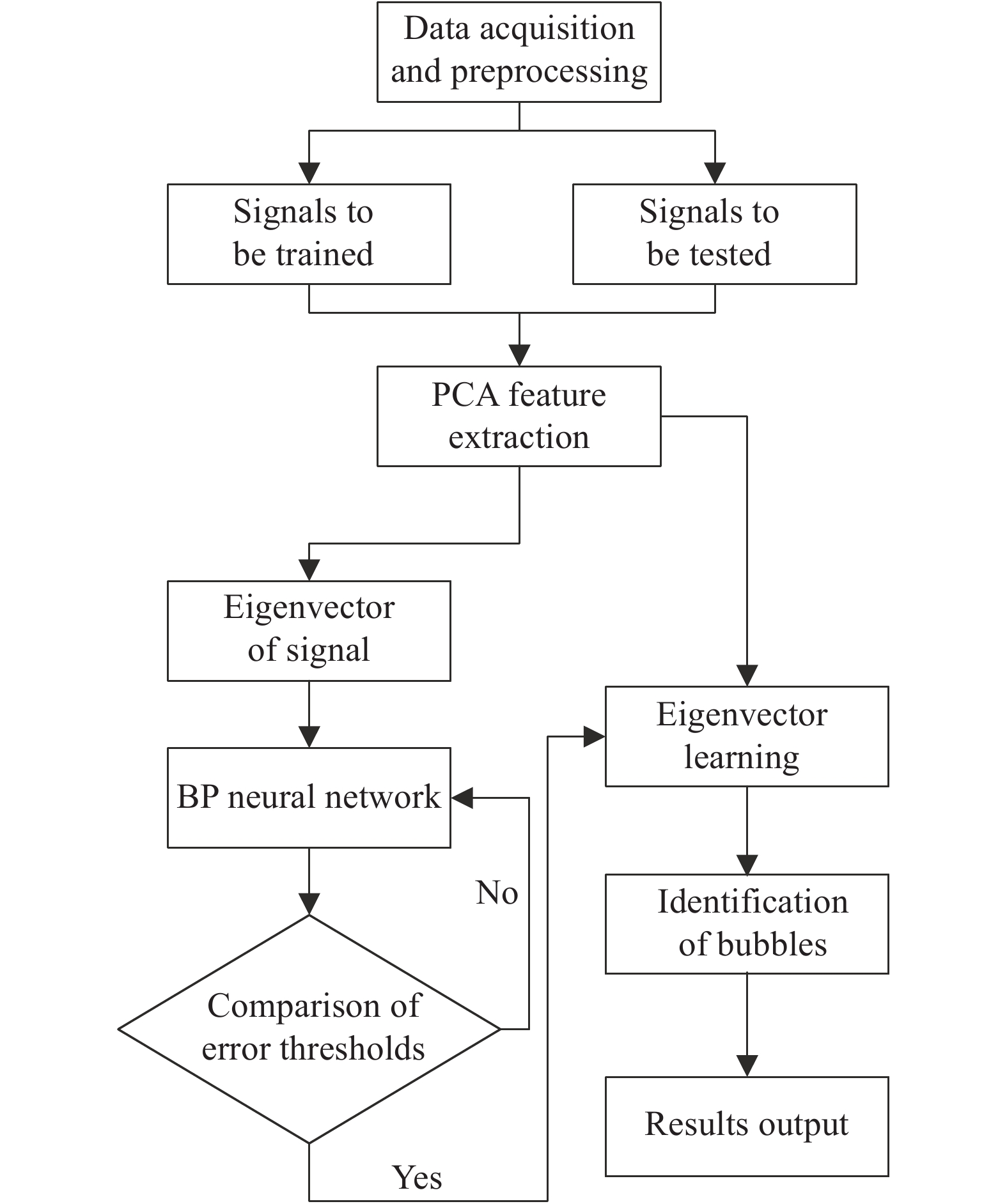
因此,利用PCA算法与弹性BP神经网络结合的气泡群识别过程如图5所示。
-
首先对隐含节点数的确定,采用经验公式[13]为:
式中:
$ j$ 为输入节点;$ l$ 为输出节点;$ a$ 为1~10之间的调节常数。文中输入神经元是经PCA提取的特征个数,为2,输出神经元个数为1,得到隐含节点范围在(3,12)之间,学习率为0.05,训练5000次,目标函数为0.001。选择不同的节点数逐个计算,每组进行7次实验取平均值,选出最优节点数,如表2所示,随着隐含节点的增加,训练次数减少,收敛用时也减少。综合考虑,确定隐含节点数为12。Number of hidden nodes Training times Convergence time/s 3 1451.71 3.43 6 1079.43 2.29 9 685.86 1.43 12 653.86 1.43 Table 2. Training of different hidden nodes
将输入层和输出层的激发函数设置为线性函数,隐含层的激发函数设置Sigmoid函数,增量因子、减量因子由实验结果所决定,其中在
$ \alpha =1.15$ ,$ \;\beta=0.55 $ 时有最优输出。无气泡、气泡和透明玻璃板分别用0、1、−1表示,输出偏差阈值设定为0.2,即输出偏差大于0.2时表示类别不确定,反之表示识别正确。 -
选择对距离激光雷达2.2 m的无气泡、气泡和透明玻璃板的回波信号共3类目标进行识别,随机选取每类各300组,共计900组数据作为训练集,另随机选取各200组共计600组作为测试集。选择特征值的不同累计贡献率,得到3组不同测试集的识别率如表3所示,选择特征值个数为2时,其识别率可以达到99.1%,累计贡献率提升到71.2%时,识别率只提高0.3%。随着特征值个数的增加,由于在识别过程中进行划分的特征维数的增加,造成特征区分不明显,最终导致识别率低。因此,在进行PCA算法和弹性BP神经网络识别的过程中,特征个数对识别结果有很大的影响。综合考虑,特征值个数为2时为最优情况。
Number of eigenvalues 2 11 28 Cumulative contribution rate 39.7% 71.2% 90.6% No bubbles(correct) 200 200 200 199 200 198 198 195 199 Bubbles(correct) 200 199 198 199 200 200 198 198 198 Glass plate(correct) 196 197 194 198 196 199 198 195 193 Recognition rate 99.3% 99.3% 98.7% 99.3% 99.3% 99.5% 99.0% 98.0% 99.0% Average recognition rate 99.1% 99.4% 98.7% Table 3. Recognition results under different cumulative contribution rates
为验证PCA算法和弹性BP神经网络结合的优越性,采用自适应与附加动量BP和无PCA进行降维的网络作为对比,对比结果如表4所示。利用神经网络对预处理的数据进行识别,弹性BP的用时明显少于自适应与附加动量BP,PCA降维的用时少于不降维时间,其中PCA+弹性BP识别率高达99.1%。对于大量水下气泡数据的进行处理时,该算法能体现出更明显的优势。
Method Recognition
rateTime(training+
recognition)/sAdaptive and additional
momentum BP98.3% 48.94 PCA+Adaptive and
additional momentum BP96.6% 10.15 Elastic BP 98.8% 1.60 PCA+elastic BP 99.1% 1.36 Table 4. Recognition and contrast results of different algorithms
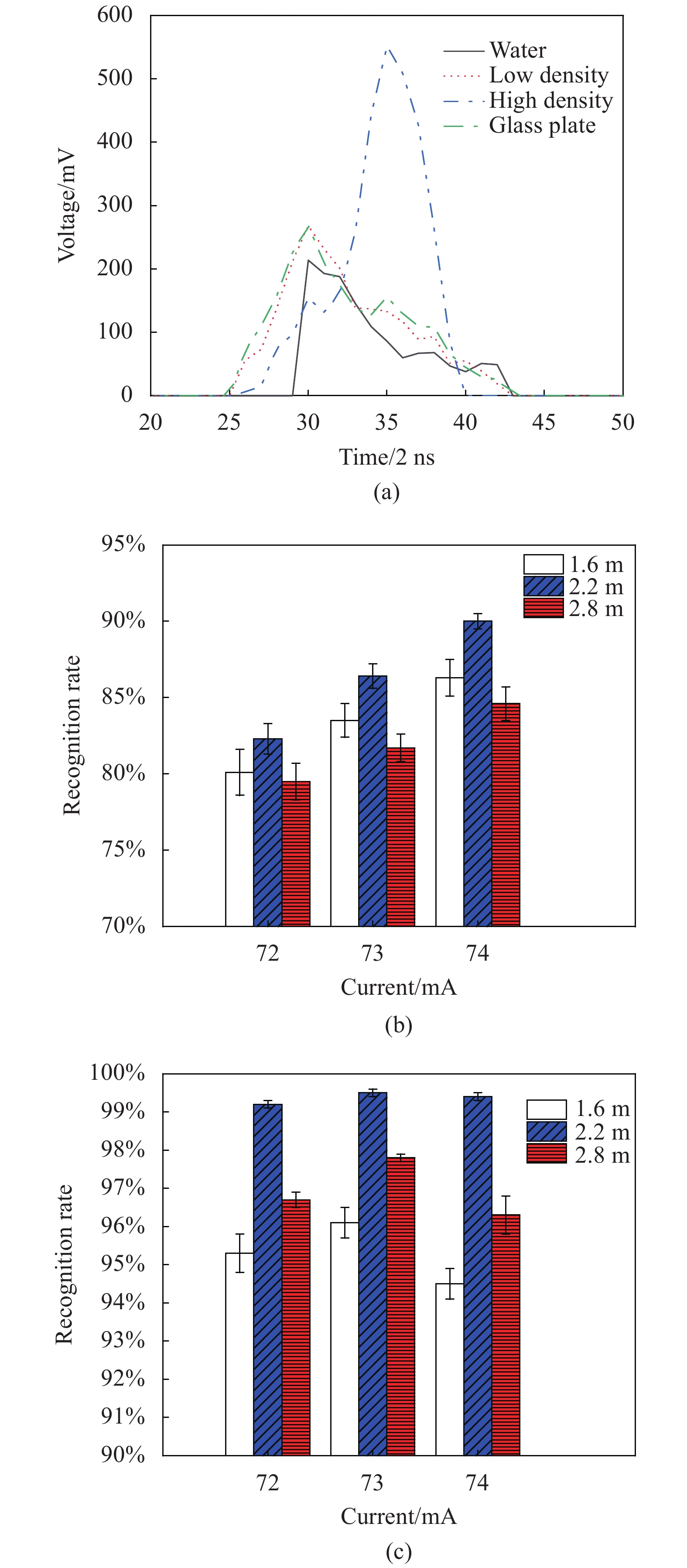
为证明该算法的泛化能力,改变激光器电流实现激光发射能量的调节,控制气阀进气量实现气泡群密度的变化,选择对距离激光雷达1.6 m、2.2 m和2.8 m的气泡群进行探测,另外选用水体和透明玻璃板的回波信号作为干扰信号。当激光器电流为72 mA,气泡群和玻璃板距离为2.2 m时,经预处理后得到的回波信号如图6(a)所示,目标的存在使得回波具有双峰现象,并且回波强度明显大于水体回波;气泡密度较小时的目标峰与玻璃板回波一致,强度小于水体回波峰;随着气泡密度的增加,目标峰值强度明显增大。

Figure 6. Echo signals and recognition results under different conditions. (a) Different targets echo curves; (b) Low density bubbles recognition rate; (c) High density bubbles recognition rate
将预处理后的气泡群回波信号与水体和玻璃板回波信号混合,随机抽取部分数据进行训练和识别。经算法处理后,得到气泡群在不同位置和激光能量下的识别情况,结果如图6(b)、(c)所示。当气泡密度较低时,由于玻璃板的回波信号与其相似,导致识别率小于高密度时的识别率约13.4%;激光器电流从72 mA增加至74 mA时,在低密度下的识别率平均提升6.3%,高密度下变化不明显。由于水体回波峰一直存在,当气泡群距离为1.6 m时,气泡回波峰与水体回波峰重叠,单峰现象明显增多,导致识别率降低;当距离增大至2.2 m时,回波信号为双峰,此时目标峰特征明显,平均识别率提升约3.5%,识别结果较为稳定;随着距离增加至2.8 m时,由于水体对激光具有强散射性质,导致回波能量较低,对气泡群回波峰的有效探测次数降低,识别率减小。
-
对于尾流气泡的探测,利用水下激光雷达进行连续采集,得到多帧动态回波信号,可以实现对非稳态气泡群的强度的检测,将原始一维信号切片预处理能减小气泡群非稳态造成的回波漂移、采样率低和无效采集等影响,利用主分量分析法对拼接的高维样本进行降维,减少了神经网络输入的维数,不但有99.1%的识别精度,还有更快的学习速度,对3类目标回波信号进行识别,结果表明PCA+弹性BP算法对水下气泡识别的有效性。改变激光发射能量和气泡群密度,实现对不同距离的气泡群探测,在有干扰信号的情况下,识别率随着气泡群密度的增大提升13.4%,在低密度下的识别率随激光能量的增加平均提升6.3%,识别率随距离的增加先增大后减小,气泡群在2.2 m时的目标峰特征明显,平均识别率提升3.5%。此次实验的样本维数太少,没有完全体现出PCA特征提取和弹性BP神经网络的优越性,后续工作将会展开大量多维样本的识别。
Underwater bubbles recognition based on PCA feature extraction and elastic BP neural network
doi: 10.3788/IRLA20200352
- Received Date: 2020-11-20
- Rev Recd Date: 2021-01-25
- Publish Date: 2021-06-30
-
Key words:
- lidar /
- bubbles recognition /
- PCA feature extraction /
- elastic BP neural network
Abstract: Aiming at the problem of difficulty in feature extraction and identification of wake echo signals detected by underwater lidar due to instability, an underwater bubbles recognition algorithm based on PCA feature extraction and elastic BP neural network was proposed. First, slice preprocessing was carried out on the echo signals collected continuously. Then the PCA algorithm was used to extract the main features of the spliced high-dimensional samples to determine the number of feature values. Then the parameters of the elastic BP neural network was selected to determine the number of hidden layer node and the number of features that can achieve optimal classification. Finally, an indoor wake detection simulation platform was used to realize the identification of bubbles and interfering targets. The experimental results show that when the hidden node is 12, the increment factor is 1.15, and the decrement factor is 0.55, two eigenvalues can be selected to classify the bubbles, non-bubbles and interfering targets. The recognition rate increases by 13.4% with the increase of bubbles density. At low density, the average recognition rate increases by 6.3% with the increase of laser energy. The recognition rate first increases and then decreases with the increase of distance. When the bubbles distance is 2.2 m, the target peak characteristics are obvious, and the average recognition rate is improved by 3.5%. Compared with adaptive and additional momentum BP, this method can reduce recognition time and achieve 99.1% accuracy. It is proved that this algorithm can be effectively and widely used in the recognition of bubbles in the ships wake by lidar.
































 DownLoad:
DownLoad: