HTML
-
近年来,受人类生产生活的影响,大气污染成为了建设“美丽中国”急需解决的问题。当污染物浓度过高时会对人类健康安全产生危害。原油在工业生产中扮演着重要角色,但作为一种化石燃料,其燃烧产生的二氧化硫是主要大气污染源之一。同时,原油中硫元素的存在也会对仓储、运输、加工设备造成腐蚀[1],形成环境污染或引发中毒等安全生产责任事故。此外,我国原油进口原产地较多,各原产地间迥异的地理、气候因素也导致了原油产品的成分差异,对原油产地实现实时溯源有助于国家对进口原油进行及时管控,保障进口能源安全,对于原油的采运、加工等具有重大的意义。目前,研究人员通常采用X-射线荧光分析法[2]、微库伦分析法[3]等方式对原油含硫量进行检测。X-射线荧光分析法[2]对石油焦样品要求高(样品的颗粒粒径小于0.15 mm,装样深度大于0.3 cm);微库仑分析技术[3]的准确度高,但燃烧段温度及氧气流量会影响测定结果。对于残碳量的测定,近年来国内外普遍采用微量法[4], 该方法对氮气纯度和氮气瓶源压力要求较高。此外,以上这些方法普遍存在操作复杂、检测时间长等局限性,使得无法满足对原油成分进行快速现场检测的需求,影响了对原油样品的快速产地溯源。
太赫兹波(Terahertz)的频率覆盖范围为0.1~10 THz的电磁波。因其低能量、高分辨率、指纹谱等特性,可广泛应用于公共安检[5]、生物医药[6]等领域。得益于太赫兹技术的特点,太赫兹光谱检测法可有效弥补传统的傅里叶变换红外光谱、X射线及近红外光谱技术[7]的不足,达到快速、准确、便捷检测的要求。在原油检测领域,研究人员已利用太赫兹技术在油气资源储量探测、石油精炼等领域开展理论与应用研究[8]。如利用时域太赫兹波谱系统分析不同产地原油的选择吸收特性阐明相应地质条件的影响,以及优化原油超声处理参数以提高油田采收及原油储运效率[9]。对原油中的两个主要成分指标含硫量和残碳量,也有多项工作报道了在太赫兹波段、近红外波段/拉曼光谱的检测结果[10-12],通过分析穿过原油样品的太赫兹脉冲的时延差及吸收系数,对原油的硫和残碳含量变化趋势进行了分析。但是,利用谱分析的方法存在样品用量大、信噪比低、精度差等缺点。
环偶极子效应于1958年首次由Zeldovich发现,用于解释弱电磁场与单粒子自旋相互作用时的宇称破缺[13]。近年来,在二维太赫兹超表面结构中成功激发了环偶极子效应,即谐振器的两个回路中的电流会沿相反的方向振荡,从而导致环形磁极子增强和电多极子受到抑制[14]。基于环偶极子效应的太赫兹传感平台已普遍用于化学和生物传感领域。与其他的太赫兹超表面物理效应例如法诺线形、电磁诱导透明或手性模式相比[15-16],环偶极子模式能够进一步增强光与物质相互作用,目前已成功应用于微痕量抗生素和病毒蛋白的检测,实验结果证明了更高的检测灵敏度和更低的物质检测下限[17]。
文中将太赫兹高灵敏度环偶极子传感器与太赫兹光谱技术结合对原油样品产地进行区分和追溯。与普通的环偶极子效应产生单环形磁场不同,文中设计的环偶极子结构采用两个镜像重叠的开口谐振器,激发新的双磁矩模式,相比单环形磁场可以进一步增强光与物质相互作用。实验中,将环偶极子超表面结合微米厚度聚碳酸酯滤膜材料,利用时域太赫兹波谱系统测量并分析不同产地原油的共振频率漂移量大小。对于不同产地的27 µm厚的原油样品,通过分别计算不同质量分数的硫元素和残碳产生的偏移量,发现总偏移量近似与以上两种指标的偏移量之和相吻合,证明了原油中影响谐振频率偏移的重要因素,可实现快速检测原油样品进行溯源的目的。因此,这种双磁矩模式提供了一种高灵敏度的检测技术,可广泛应用于原油的定性和定量检测中。
-
图1(a)为所设计结构的几何示意图,该结构是由两个带有单间隙的环形金属带交错重叠组成的,单元结构沿X、Y轴周期性地排列以形成阵列,每个单元结构的周期为200 μm×160 μm。仿真计算表明,当参数d从10 μm变化到30 μm时,谐振谷的Q值保持在8.5~9左右。因此笔者选择了d=10 μm来缩小超表面芯片的大小。优化后的几何参数如下:g=4 μm,w=5 μm,R=40 μm,d=10 μm。超表面通过单步光刻制造,随后通过热沉积镀上金膜。由金膜制成的图案(厚度为200 nm)附着在厚度为22 μm聚酰亚胺柔性衬底上。结构中的双磁矩模式被垂直于超表面平面(Z轴)入射的太赫兹波激发,其电场极化(Ey)沿间隙(Y轴)方向。

Figure 1. (a) Unit cell of dual torus toroidal structure; (b) Transmission spectrum at 0.551 THz; (c) Schematic diagram of toroidal dipole formation; (d) Far-field scattering power of multipole
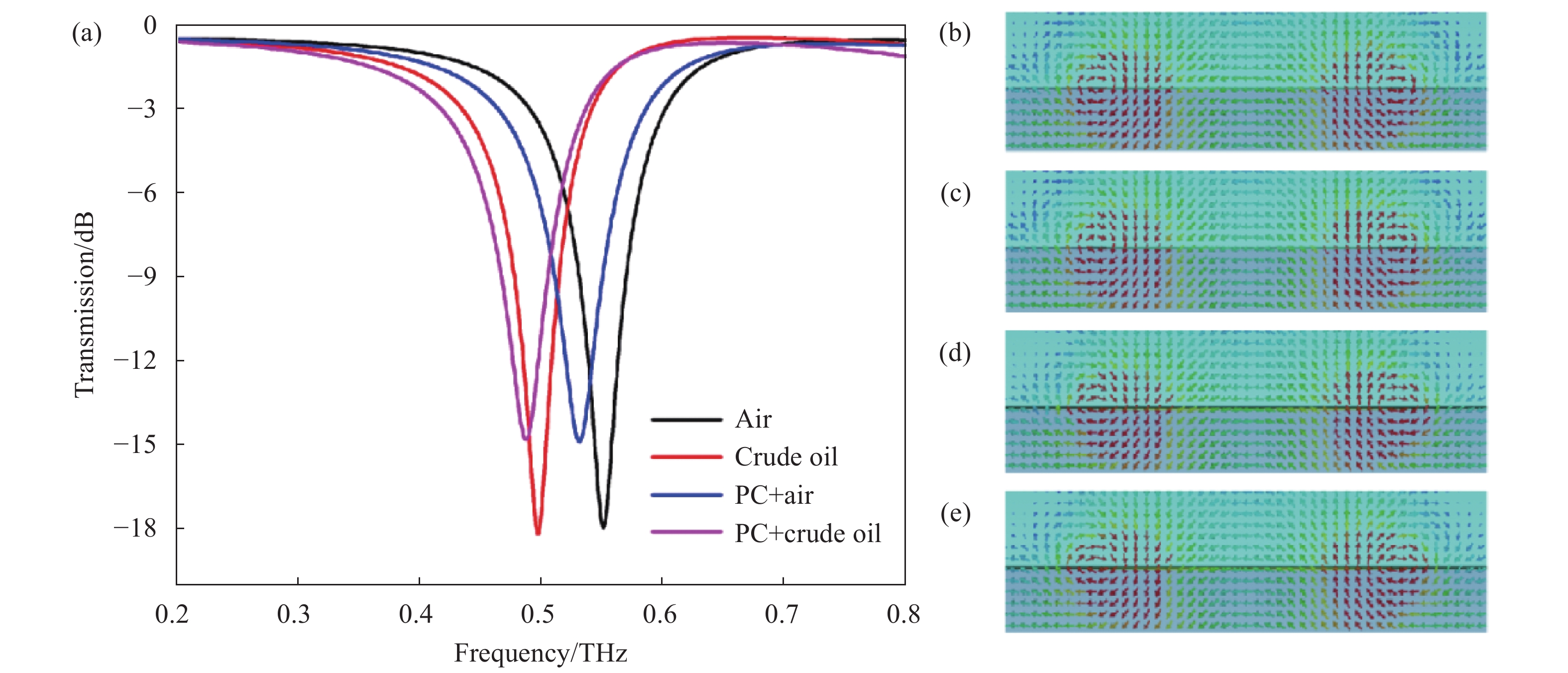
利用CST微波工作室仿真工具,基于有限元法对结构进行了全波电磁仿真,并研究了双磁矩模式共振的机理。首先在单元上设置了沿X、Y轴方向的条件边界条件,沿Z轴方向设置了开放边界条件,计算了所设计的双磁矩模式的透射谱,如图1(b)所示。在0.551 THz处观察到明显的共振。为研究此共振的特性,笔者对其共振频率下的表面电流进行了数值模拟,如图1(c)所示。最左侧月牙型环路与右侧圆形开口谐振环路的表面电流分别以顺时针和逆时针的方向流动(蓝色箭头),产生方向相反的两个磁场,形成左侧首尾相连的闭合磁场,从而沿Y方向引起环形磁矩;由于镜像对称,最右侧月牙型环路与左侧圆形开口谐振环路的表面电流分别以逆时针和顺时针的方向流动(紫色箭头),形成的两个方向相反的磁场首尾相连,在右侧激发另一个环形磁矩。与大多数环偶极子超表面结构中单环形磁场模式相比,所设计的超表面支持新的双磁矩模式,从而可以进一步增强光与物质的相互作用。
结构的多极矩的远场散射功率计算公式为[18]:
式中:第一项表示电偶极矩Px远场散射能量;第二项表示磁偶极矩Mz远场散射能量;第三项为环偶极矩Ty远场散射能量、第四项为电四极矩Qe远场散射能量;第五项为磁四极矩Qm远场散射能量。图1(d)给出了多极子的远场散射功率[19],通过计算电偶极子Px,磁偶极子Mz,环形偶极子Ty,总四极子Q(电四极子Qe和磁四极子Qm之和)的远场散射功率可以看出,在共振频率附近,电磁偶极子和电四极子都被强烈抑制,环偶极子占主导地位。
接下来,利用双磁矩结构仿真了两种检测方法:(1)直接将原油样品滴覆于结构表面上,即原油样品层与超表面结构无缝贴合;(2)在超表面结构上无缝贴合一张聚碳酸酯滤膜,随后将原油样品滴覆于滤膜上。这里假定原油样品的折射率为1.4[20]。对于超表面结构上27 μm的原油样品有(无)滤膜的情况进行了模拟,如图2(a)所示,传感器的灵敏度按照公式(2)计算,得:
根据理论仿真结果,当折射率n从1(空气)变化到1.4(原油)时,对于第1种检测方法,谐振频率f的漂移为54 GHz,计算出的灵敏度为135 GHz/RIU。而对于第2种检测方法,谐振频率漂移为49.2 GHz,计算出的灵敏度为123 GHz/RIU,由此可见,检测中引入滤膜对检测灵敏度产生的影响较小。图2(b)~(e)所示为图2(a)中4种情况下共振频点处的磁场图,4个频点处的磁场强度相差很小。由于滤膜可以有效保护高灵敏检测芯片不被原油污染,在下面的实验中利用滤膜上加原油样品的方法进行太赫兹测试及分析。
-
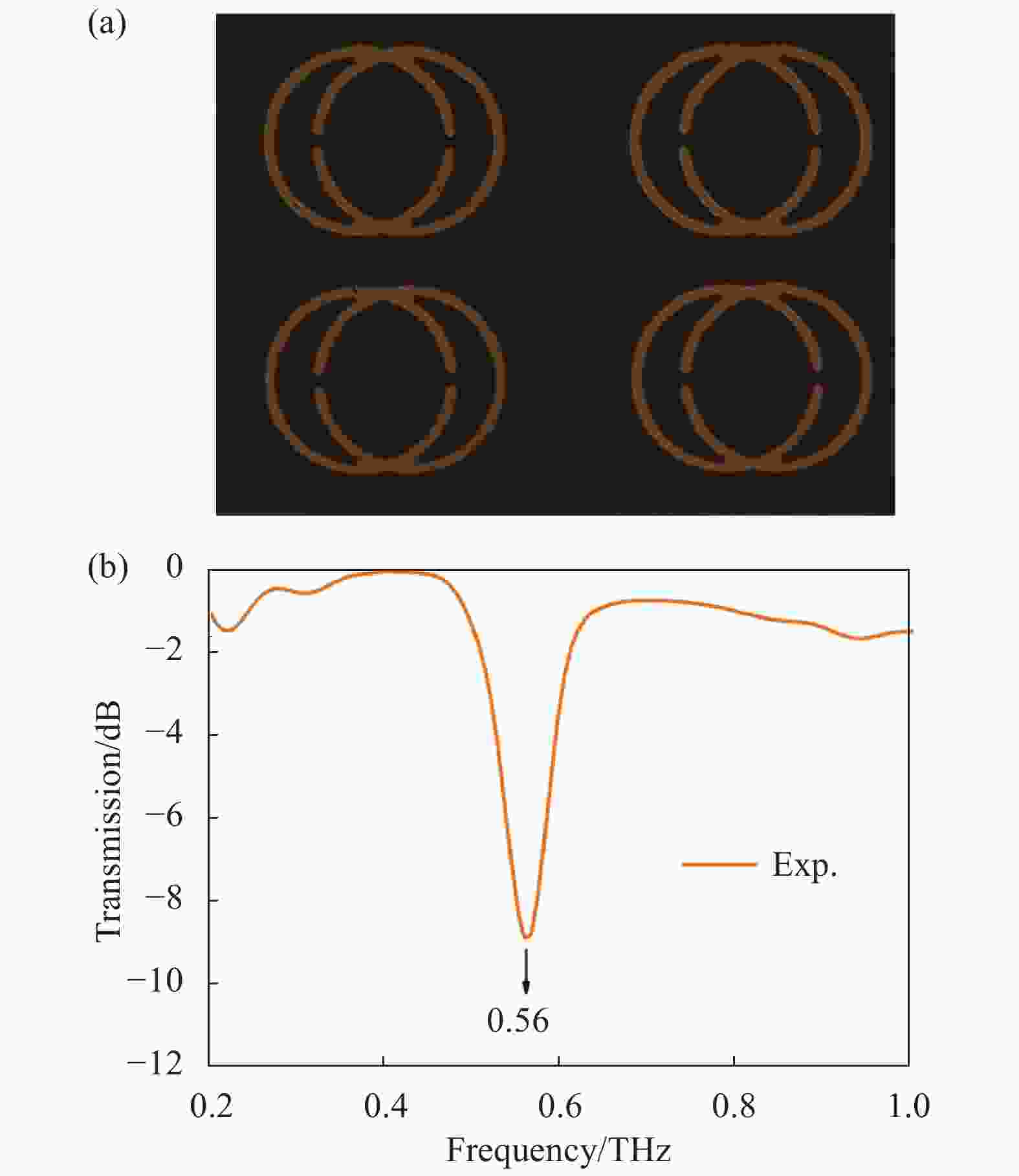
根据所上述理论参数,加工后的芯片的部分结构的光学显微镜图像如图3(a)所示。笔者采用的实验装置为太赫兹时域光谱系统(Advantest TAS 7400)。芯片所测得的太赫兹光谱如图3(b)所示,所设计得结构得谐振峰的中心频率位于0.56 THz处,与仿真结果吻合,仿真与实验的误差主要来源于通过热沉积方法制造的金属谐振器粗糙边缘的散射损耗和柔性样品图案可能的不均匀性。
-
不同产地的原油样品均从海关获取。12个原油样品标号分别为2-2,2-5,3-4,3-5,4-2,4-4,5-5,5-6,6-3,6-4,9-2,9-5,其产地包括巴西图皮地区、伊朗、科威特、安哥拉KISSANJE、俄罗斯东西伯利亚,以及俄罗斯萨哈林岛。将12种来自不同地区的原油样品取5 mL出来分装至试管中,并标号记录信息。再将12种不同产地的原油样本放置于高速冷冻离心机设备进行离心操作,离心时间为10 min,速度为20000转/s,如图4(a)所示。离心后的原油样品如图4(b)所示。然后再用电动移液枪每次取10 μL滴在滤膜上,其中通过固定移液枪的高度来确保每次样品的覆盖面积为边长约为1 cm的正方形范围,使得样本厚度与样本量呈线性关系。再将离心后的样品按照图5(b)~(g)所示的实验步骤形成带芯片的原油检测样品腔(长2.5 cm,宽2.2 cm),放入太赫兹时域光谱系统(Advantest TAS 7400)中进行检测,系统动态范围为~60 dB,其有效光谱范围为0~3 THz,分辨率为1.9 GHz。每个样品重复测量3次,得到误差条,所有测量都低于3%的环境湿度下进行。

Figure 5. (a) Experimental schematic diagram based on the dual torus structure; (b)-(g) Experimental procedure diagram
图5(a)为基于双磁矩结构进行实验的示意图,上下则为聚四氟乙烯制成的前凸盖和凹底,整个腔体放置于太赫兹时域光谱系统发射器和接收器之间。具体的实验步骤图如图5(b)~(g)所示。
-
图6(a)中显示的是具有双磁矩结构超表面的原油检测的实验归一化振幅透射谱图。从图中可见,2-2号~9-5号原油样品中,每一种原油都对应特定的双磁矩谐振频率。原油里两个最主要的指标为硫含量和残碳量[12],而密度是与残碳量指标密切相关。此外,所获取的原油样品均经过了脱水处理以及去除沉淀物和机械杂质,盐,钒和镍含量均为ppm量级,对实验结果不会产生很大影响。图6(a)中各产地原油双磁矩谐振频率漂移量的相对值如图6(b)中紫色柱体所示。从紫色柱体可以看出,相同产地的原油的谐振频率平均值相对差值平均为4.63%,不同产地的原油的谐振频率平均值的相对差值平均为56.53%以上,从实验结果可明显区分出原油的产地。

Figure 6. (a) Experimental transmission spectrum; (b) Bar graph of the relationship between full frequency shift and single frequency shift in the mixture; (c) Frequency shift point diagram and linear fitting diagram of sulfur content; (d) Frequency shift point diagram and linear fitting diagram of residual carbon content
为了进一步分析不同产地原油的双磁矩谐振频率漂移量的差异产生的原因,理论计算了原油中不同含硫量的样品产生的频率漂移的值。原油中的硫未提炼加热前80%的形式为硫醚[10],且硫醚中的硫的质量分数是固定的,因此硫含量随硫醚的质量分数而依次上升,不同质量比的硫醚和原油呈现不同的介电系数。根据参考文献[10]中的不同硫含量的原油介电系数的差异,代入CST软件中,可以理论得到图6(c)中频率漂移值与硫含量的对应关系。从图6(c)中可以看到两者有着很好的线性关系。利用海关给出的样品测出的标准硫含量数据,根据图6(c)中的理论计算关系得出了不同产地原油仅硫含量的差异对应的频率漂移值,如图6(b)橙色柱状图所示。此外,12种原油样品的残碳值较低(小于10%),说明其主要成分为少环芳烃,不含多环芳烃和沥青等物质[1]。由参考文献[21]可知,由于H/C比值的大小主要取决于少环芳烃,使得残炭值与其H/C原子比值成正比,不同H/C比值对应于不同的折射率。笔者可通过在原油样品上方叠加不同折射率的分析物,来模拟原油中不同含量的残炭值对双磁矩谐振频率漂移量的影响,如图6(d)所示。图中残炭含量在1~10%内变化和20%~80%范围的变化呈现不同的线性关系,这与参考文献[21]中的图5相匹配。笔者将海关通过微量法得到的不同产地原油的残碳量数据,代入图6(d)进行理论计算,得到频移量,并在图6(b)中用绿色柱子表示,其中R是计算结果与实验结果之间的偏差百分比。理论仿真的结果和实验结果证明了总漂移近似由原油中的硫元素和残碳分别产生的频率漂移的叠加,同时说明可以通过透射谱图来对原油进行检测并溯源。
-
文中设计了一款基于双磁矩环偶极子的高灵敏太赫兹检测芯片,并将其应用于原油产地检测。笔者将芯片结合时域太赫兹波谱系统,通过原油中两个最主要的指标硫含量和残碳量测试了不同产地原油样品的太赫兹光谱。根据芯片的测试结果可知:(1)不同产地的原油的谐振频率平均值的相对差值平均为56.53%,相同产地的原油的谐振频率平均值的相对差值平均为4.63%,从实验结果可明显区分出原油的产地;(2)芯片的谐振频率的总漂移近似为由原油中的硫元素和残碳分别产生的频率漂移的叠加,因而笔者可以通过透射谱图来对原油进行检测并溯源。仿真和实验结果表明:笔者所设计的太赫兹检测芯片提供了一种高灵敏度的检测技术,它不仅限于原油的检测与溯源,更可广泛应用于生物分子实时监测或探测化学物质成分检测、产地溯源等领域。
致 谢 作者感谢上海海关刘曙老师提供了原油样品及检测参数。











 DownLoad:
DownLoad: