-
当前,越来越多的国家开始提出并建设大规模卫星星座,如星链(Starlink)低轨互联网卫星星座、OneWeb卫星系统、O3b卫星系统、亚马逊Kuiper太空星座计划等,仅Starlink星座计划就包括4.2万颗卫星,大规模卫星星座建设对未来太空环境安全、空间资源利用带来巨大挑战。世界上主要的航天大国已经意识到空间资源对国家军事安全、国民经济发展等方面的重要战略意义,并不断推进空间目探测和监视技术的发展[1-3]。
空间目标一般包括卫星、空间碎片、小行星等,目标尺寸小,探测距离远,目标反射能量弱,因此通常称之为暗弱空间目标。对空间暗弱目标的亮度目前没有严格定义,通常可认为亮度低于13星等的为暗弱目标,约相当于在1000 km距离观测10 cm目标的亮度。空间目标探测包括地基探测系统和天基探测系统,地基探测系统虽然技术成熟,但是受气象、地域、时间等条件影响大,探测效能受限。天基探测系统搭载于卫星平台,不受气象条件、地理位置以及大气传输的影响,具有全天时、全天候、高灵敏度、无覆盖盲区的巨大优势,是当前空间目标探测的重要手段之一[4-7]。
基于微纳卫星平台的天基空间目标探测系统具有网络化部署实现大范围高频观测以及综合成本低的优势,因此得到快速发展。当前国外天基空间目标探测系统已大量采用微纳卫星平台,如加拿大MOST卫星[8]、Sapphire卫星[9]、NEOSSat卫星[10-11]、STARE卫星[12]等,均采用微纳卫星平台,载荷质量数十公斤、整星重量在百公斤量级左右,暗弱目标探测能力通常可以达到13星等以上。
根据国外的应用情况,天基空间目标探测相机大量采用可见光波段,利用可见光波段开展空间目标探测有诸多优势:(1)大多数空间目标在可见光波段的特性较强,易于探测;(2)可见光探测波长短,探测精度更高;(3)被动探测,隐蔽性好,能耗低;(4)易于轻小型化,实施成本低;(5)图像处理技术成熟,易于开展各项应用[13]。
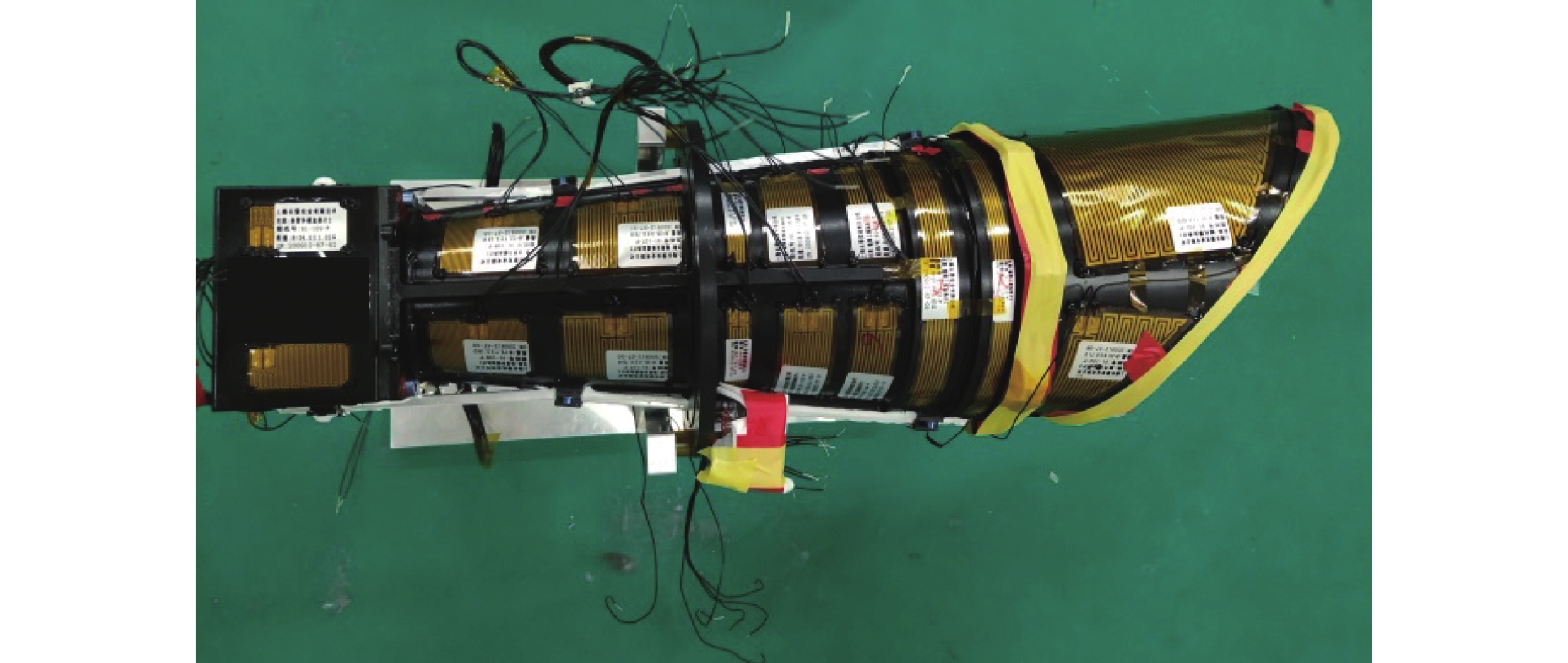
文中设计开发了一套轻小型、大视场、高灵敏度空间目标探测光学相机,探测星等优于13星等,探测视场8°×8°,质量5 kg,可广泛部署于微纳卫星平台或寄宿于大卫星,发挥集群探测优势,实现对空间碎片、小行星等暗弱空间目标的大范围、高灵敏、高频次探测,为空间碎片碰撞预警、小行星研究与预警提供高实时性数据支撑。
-
系统性能指标如下:
(1)工作波长:0.4~0.7 μm;
(2)视场覆盖:8°×8°;
(3)角分辨率:14″;
(4)可探测星等:优于13星等;
(5)质量:≤5 kg。
可探测星等是评价空间目标探测相机性能的核心指标,其影响因素包括目标辐射特性、探测相机性能以及数据处理能力。远距离探测的目标通常表现为暗弱点目标,通常要求图像信噪比大于6,以实现有效探测[14-15]。根据信噪比以及探测系统性能要求,分解系统设计指标,开展方案设计。
-
空间碎片、小行星等暗弱空间目标信号能量主要来自本体对太阳光的漫反射作用,其亮度以星等来描述,可表示为:
式中:mobj为目标星等;msun为太阳星等,msun=−26.74;d为目标尺寸;R为目标与探测相机距离;ρdiff为目标反射率;pdiff (θ)为散射相位角函数。
对于球形目标,目标散射相位角函数表示为:
式中:
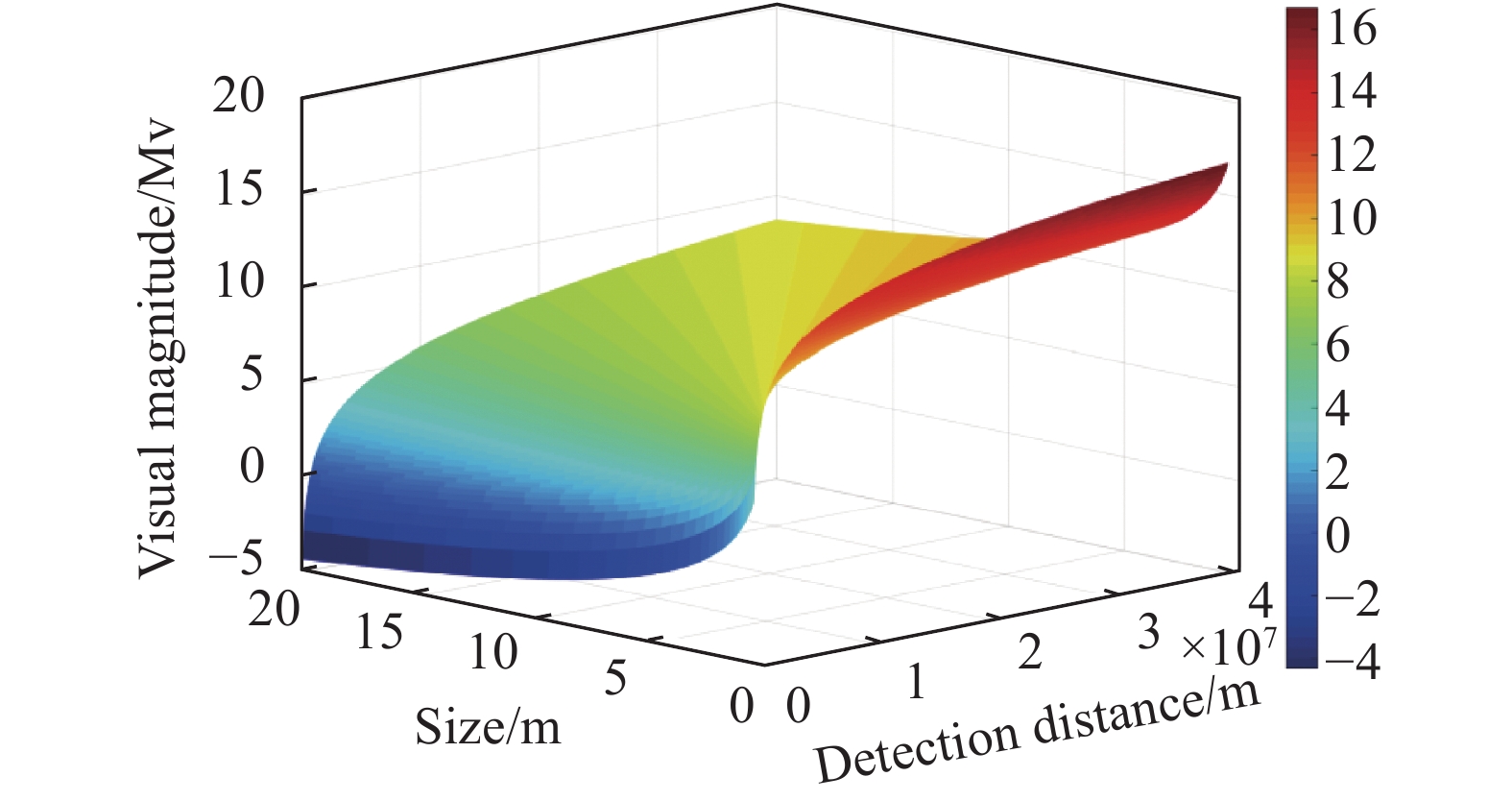
$ \theta $ 为太阳与空间目标连线、空间目标与探测相机连线形成的夹角,如图1所示。由公式(1)和公式(2)即可得到一定相位角条件下、不同尺寸空间目标在不同探测距离上的亮度。以相位角45°为例,空间目标亮度与尺寸、探测距离的关系如图2所示。可以看出,达到13等星探测能力相当于在1000 km距离探测到直径10 cm的目标。
目标的星等也可由目标辐照度表示为:
式中:Esun为工作波段太阳对目标的辐照度,可由普朗克黑体辐射定律得出;Ereflect为目标辐照度。利用该公式可建立探测系统信噪比与可探测星等的关系。
-
可见光波段点目标探测系统信噪比可表示为:
式中:esignal为信号电子数;enoise为噪声电子数。
信号电子数由目标反射太阳光,经光学系统收集、探测器光电转换后产生,可通过简化公式表示为:
式中:D为探测相机镜头有效通光孔径;τ为镜头光学效率;K为偏落因子;λ为平均波长;h为普朗克常量;c为真空光速;QE为探测器量子效率。
空间目标探测的噪声主要来源包括光子噪声、暗电流噪声、读出噪声、背景噪声、量化噪声等,总的噪声电子数可表示为:
式中:en_ph为光子噪声;en_bg为天光背景噪声;en_d为暗电流噪声;en_cir为电路噪声;en_r为读出噪声;en_AD为量化噪声[16-17]。
结合公式(4)~(6),空间目标探测系统信噪比可表示为:
式中:工作波段太阳对目标的辐照度Esun=526.3 W/m2;镜头光学效率τ=0.64;偏落因子K=0.4;平均波长λ=0.54 μm;普朗克常量h=6.63×10−34 J·s;真空光束c=3×108 m/s;量子效率QE=0.8;积分时间t=2 s。由此可评估探测系统口径、探测星等、信噪比的关系。
将以上数据代入公式,可以得到探测系统口径、探测星等、信噪比的关系,如图3所示。
在满足信噪比要求的前提下,实现13星等探测能力的镜头口径越小,探测系统质量越轻。经计算分析,镜头口径70 mm时,可以实现13星等探测能力,探测信噪比6.1,满足性能要求,据此进行系统设计。此外,在卫星姿态稳定度较高的情况下,可以通过延长积分时间进一步提高极限星等探测能力。
-
为提高系统性能,需要设计大视场大相对孔径的光学系统。根据探测器选型、像质、接口与工程实现等要求,总结光学系统设计指标要求如下:
(1) 光谱范围:0.4~0.7 μm;
(2) 口径:≥70 mm;
(3) 视场:≥8°×8°;
(4) 透过率:≥0.8;
(5) 能量集中度:≥80%@11 μm;
(6) MTF:≥0.6@45 lp/mm;
(7) 像面相对照度:≥90%。
-
由设计指标可以看出,该镜头具有大相对口径以及大视场的特点。反射式系统虽然有体积、质量优势,但通常视场角较小,并且同轴系统存在遮拦,无法选用。综合考虑光学系统的特点、工程实现性、成本等因素,光学系统选择透射式结构。
由于Petzval镜头适用于大孔径、小F数的应用场景,并且能够实现相对较大的视场,因此选择Petzval镜头形式作为初始结构进行优化设计。结合相机的应用条件,在优化过程中重点考虑以下问题:
(1)以提高能量集中度为目标进行镜头优化,提升暗弱目标信号收集能力;
(2)优化过程中对镜头长度进行控制,减小镜头体积;
(3)对玻璃材料进行优化,选低密度材料;
(4)减小胶合透镜的使用,避免太空环境下光学胶老化引起透过率下降。
-
光学系统共由八片透镜组成,单片透过率达0.995/cm以上,整体透过率达0.83以上。镜头最大透镜尺寸82 mm,焦距161.6 mm,相对孔径为2.3∶1,视场角8°×8°,系统总长度为280 mm,后截距为6.5 mm。结果均满足或优于设计指标要求。
光学系统的MTF曲线如图4所示,全视场平均MTF大于0.75。
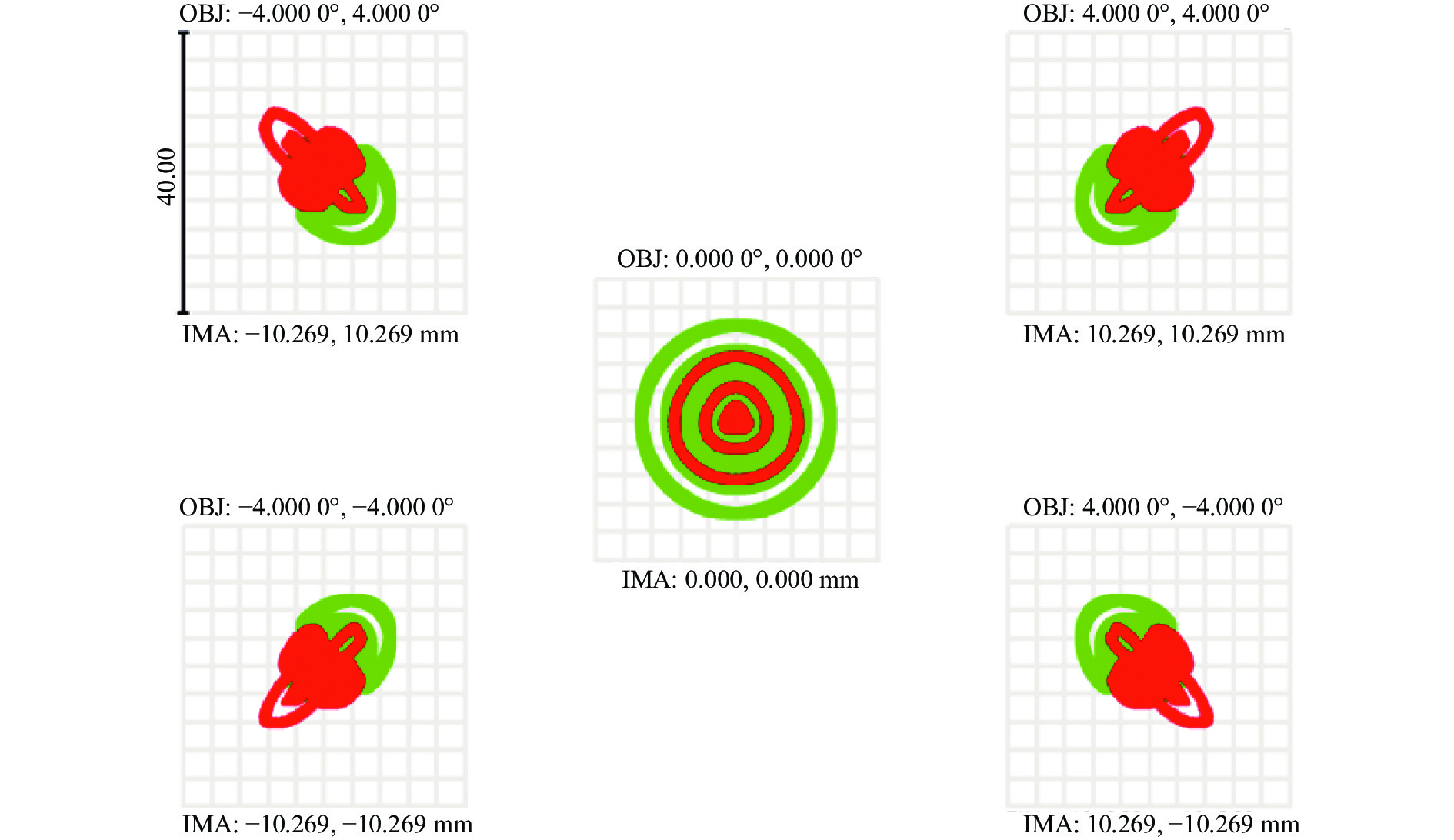
光学系统点列图如图5所示,全视场最大弥散斑RMS半径小于3.81 μm,大部分能量集中到单个像素内,光斑形状较好。
光学系统能量集中度如图6所示,全视场平均能量集中度达到90%,单个像素可收集点目标的大部分能量,提高点目标的探测能力。
-
随着空间活动的日益频繁,实时掌握空间态势对于安全的发展空间、利用空间至关重要。基于微纳卫星开展空间态势感知是一种高效费比的途径,国外已发射多个光学载荷验证了基于微纳卫星开展暗弱空间目标探测的技术可行性。面向微纳卫星平台空间目标探测的应用需求,设计、研制了一套轻型高灵敏暗弱目标探测光学相机,质量5 kg,探测视场8°×8°,并通过地面试验验证可以实现优于13星等的探测能力。该相机可广泛部署于微纳卫星平台,通过组网实现对暗弱空间目标的大范围、高灵敏、高频次探测,为我国空间碎片研究、航天器碰撞预警提供高实时性数据支撑。
Lightweight and high-sensitive optical camera technology for faint space target detection
doi: 10.3788/IRLA20220709
- Received Date: 2022-10-18
- Rev Recd Date: 2022-12-09
- Publish Date: 2023-05-25
-
Key words:
- space-based optical camera /
- faint target /
- space debris /
- micro-satellite
Abstract:




















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: